Allopurinol Tumor Lysis Syndrome
Allopurinol tumor lysis syndrome. Risk assessment and prophylactic therapy is critical in preventing this oncological emergency. Stewart Cameron George S. Hyperuricemia hyperkalemia hyperphosphatemia and hypocalcemia.
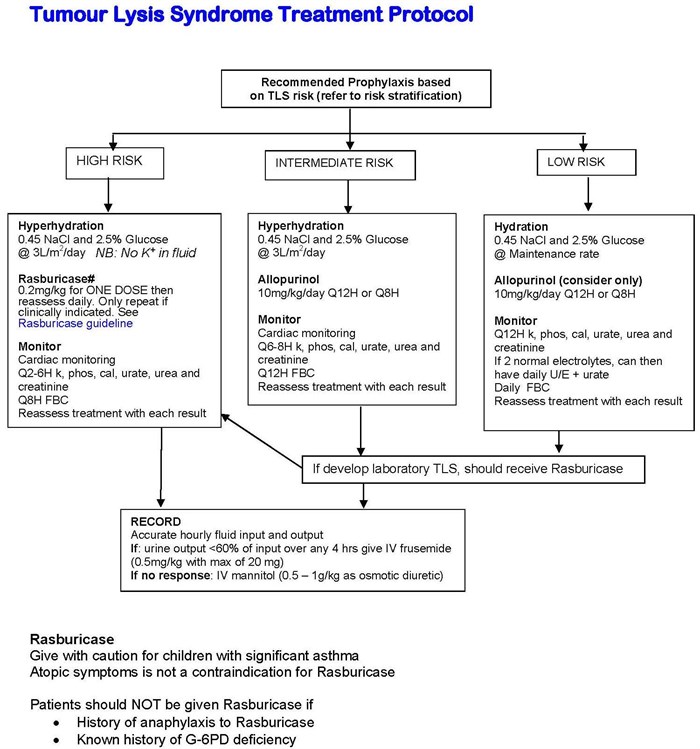
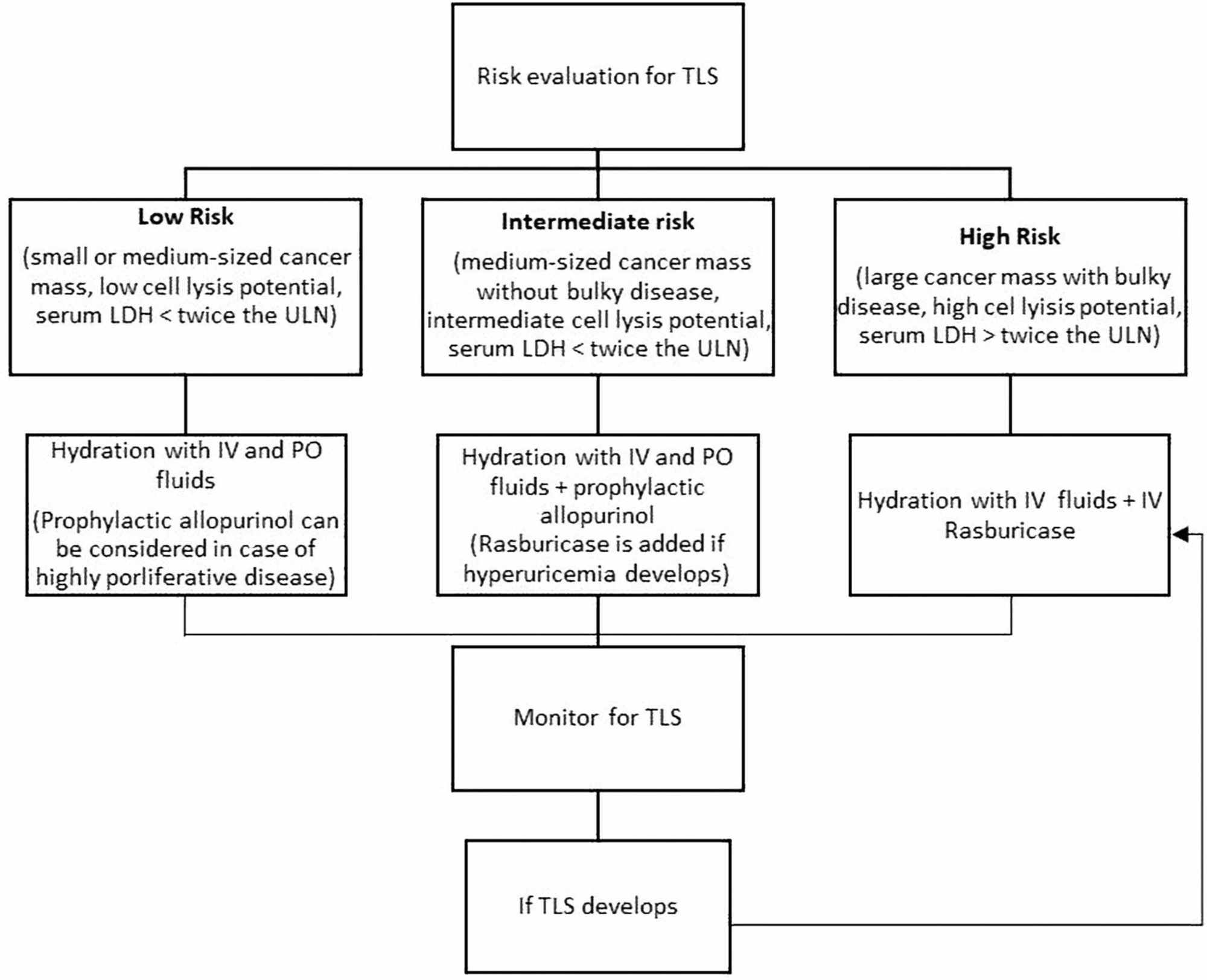
1 See Appendix A for stratification based on risk factors 2 Adequate hydration should be based on clinical judgment and monitoring including urine output. 160 1986 189-195 Eisevier CCA 03541 189 Allopurinol in renal failure and the tumour lysis syndrome H. Davies Purine Laboratory and Renal Unit Guys Hospital London Bridge London SEI 9RTUK Received 1 May 1986.
Morris and Philip M. Tumor Lysis Syndrome TLS in Adult Patients Page 1 of 7. It is usually given orally at 600 mg daily for prophylaxis and 600-900 mg daily up to a maximum of 500 mgm 2 daily for treatment of tumor lysis syndrome.
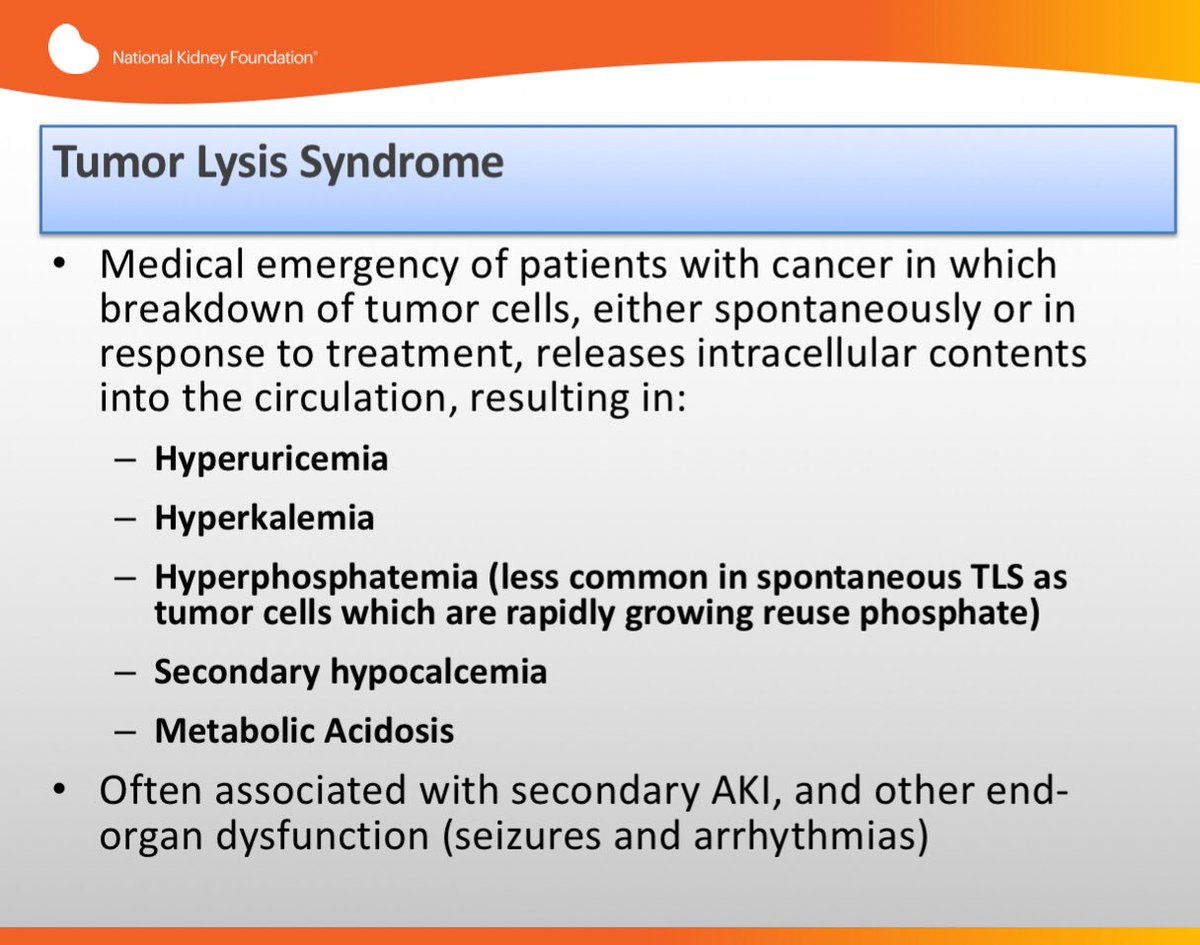
The aim of the study was to evaluate the effects of rasburicase versus allopurinol on plasma uric acid creatinine and phosphorus levels in paediatric patients with TLS. Tumor lysis syndrome TLS is an oncological emergency characterized by a classic tetrad of hyperuricemia hyperkalemia hyperphosphatemia and hypocalcemia. It is very easy to give too much allopurinol.
Treatment of established TLS involves aggressive hydration electrolyte management and the use of. In FLORENCE 346 patients with hematologic malignancies at intermediate to high risk for tumor lysis syndrome were randomized to receive 120 mg of febuxostat or 200-600 mg of allopurinol daily. Etc are the result of overdosage due t.
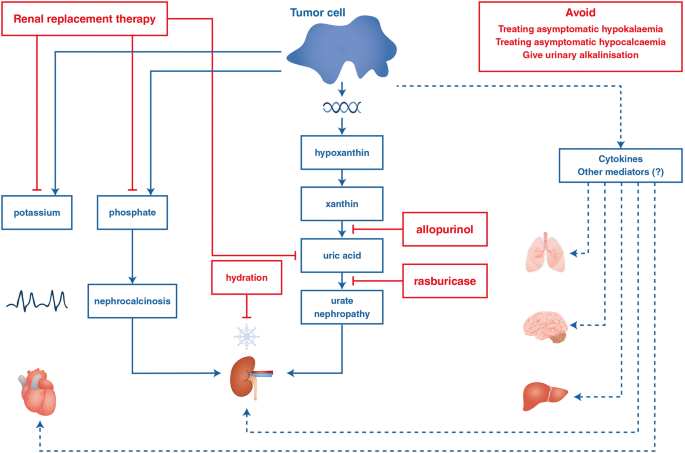
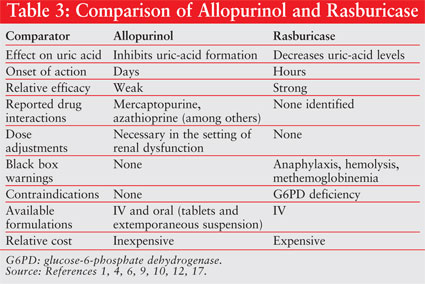
Allopurinol is a medication which inhibits xanthine oxidase. Uric acid and Xanthine are both potentially nephrotoxic due to precipitation in the renal tubules. Allopurinol in renal failure and the tumour lysis syndrome Clin Chim Acta.
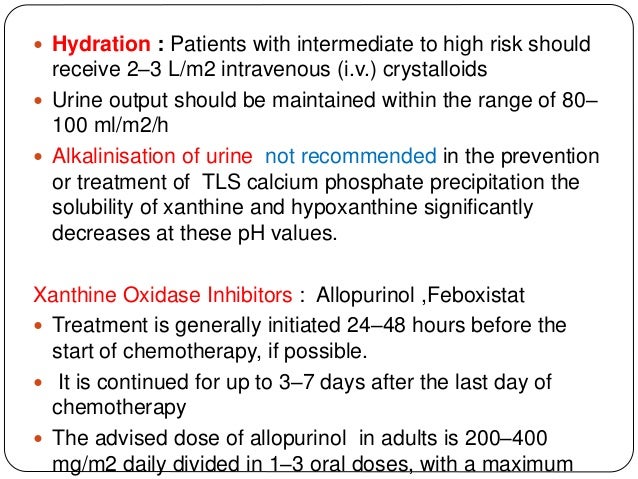
Maximum daily dose of allopurinol is 800 mgday. Hyperuricaemia accompanying tumour lysis syndrome TLS is a serious complication in neoplasias with rapid proliferation and cellular destruction.
Maximum daily dose of allopurinol is 800 mgday.
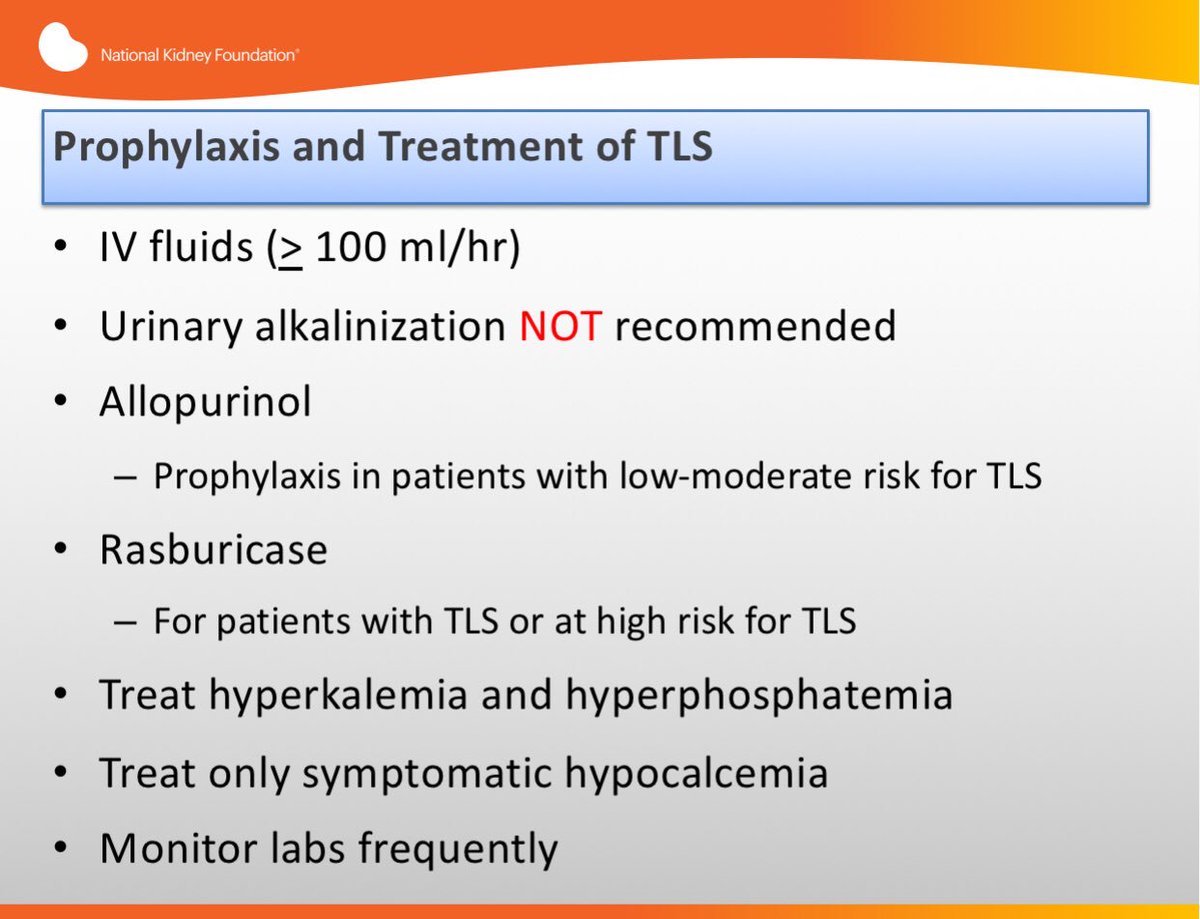
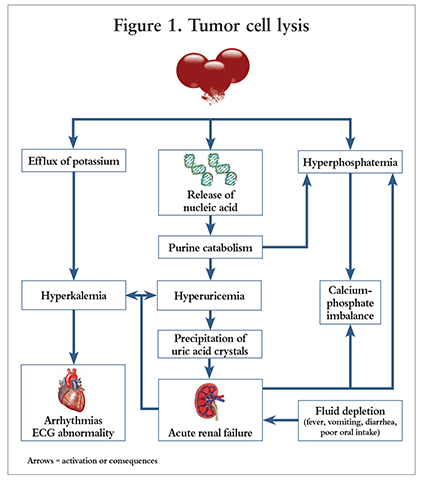
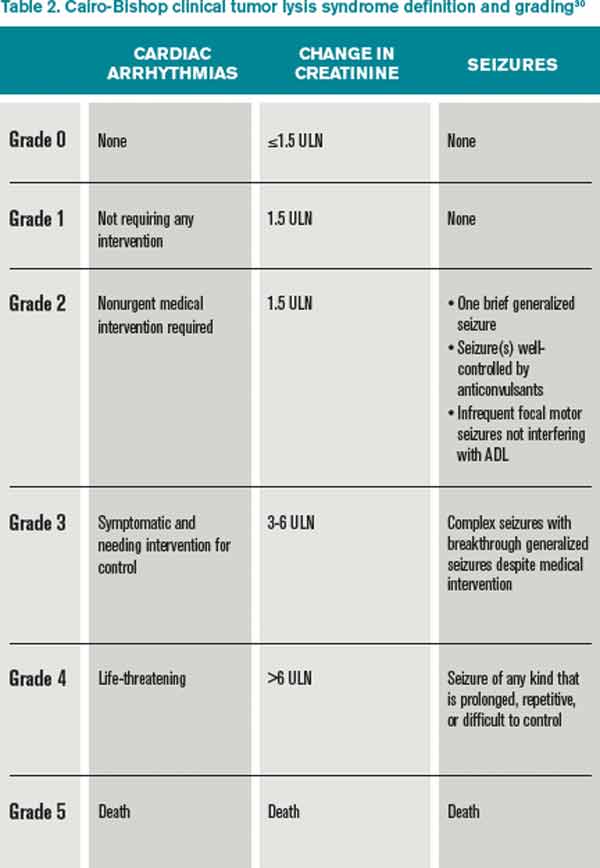
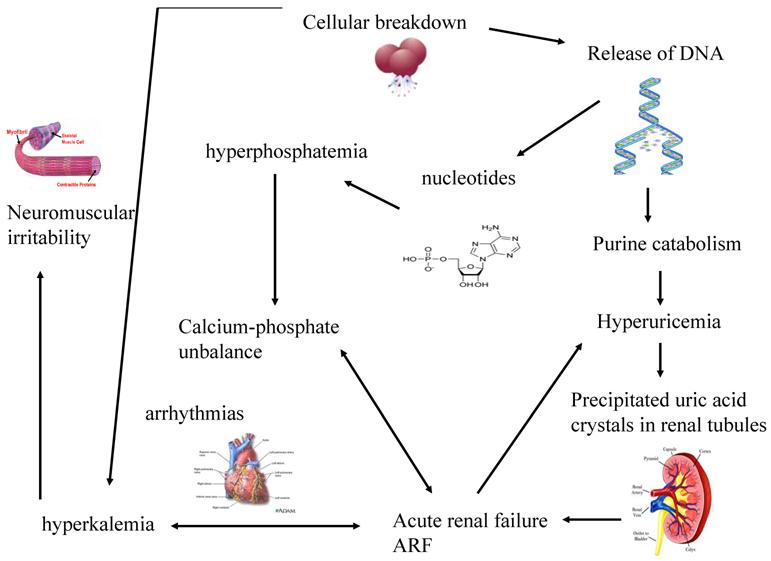
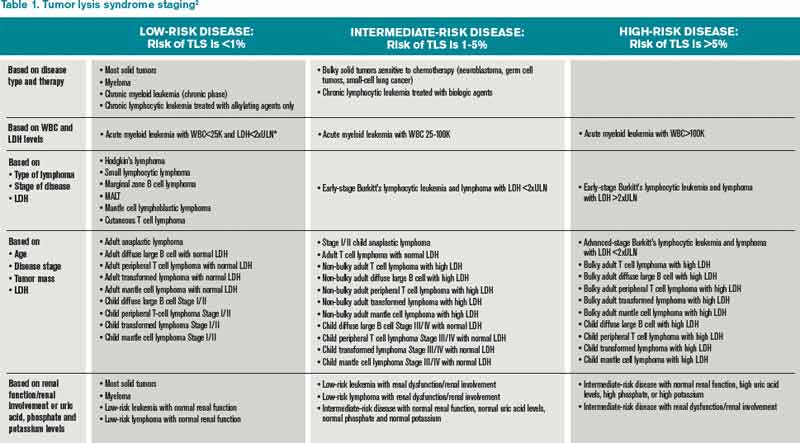
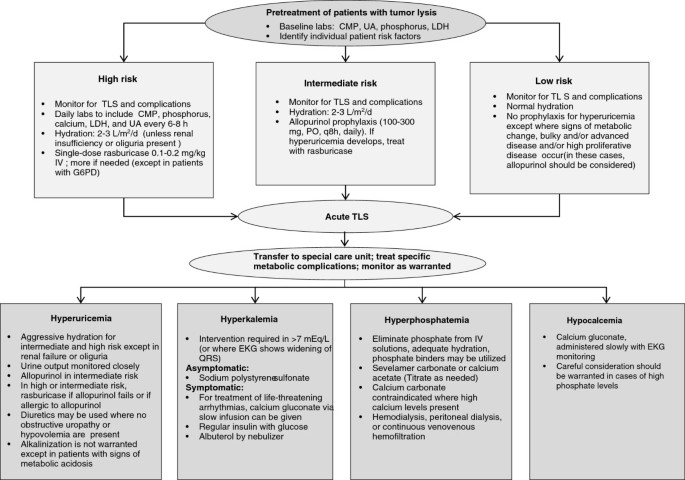
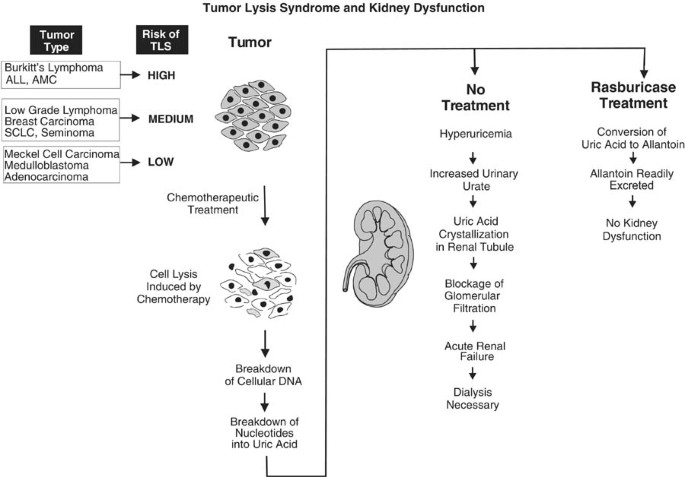
Uric acid and Xanthine are both potentially nephrotoxic due to precipitation in the renal tubules. This paper illustrates several important points relating to the use of allopurinol in renal failure or situations of purine overproduction. It is very easy to give too much allopurinol. TLS is characterized by the rapid development of hyperkalemia hyperphosphatemia hypocalcemia and hyperuricemia and is potentially life-threatening. Maximum daily dose of allopurinol is 800 mgday. Uric acid has a greater tendency to precipitate and to cause renal damage. Tumor lysis syndrome TLS is an oncologic emergency that is caused by massive tumor cell lysis with the release of large amounts of potassium phosphate and nucleic acids into the systemic circulation. Hyperuricaemia accompanying tumour lysis syndrome TLS is a serious complication in neoplasias with rapid proliferation and cellular destruction. Tumor lysis syndrome TLS is an oncological emergency characterized by a classic tetrad of hyperuricemia hyperkalemia hyperphosphatemia and hypocalcemia.
Davies Purine Laboratory and Renal Unit Guys Hospital London Bridge London SEI 9RTUK Received 1 May 1986. Hyperuricemia hyperkalemia hyperphosphatemia and hypocalcemia. Laboratory tumor lysis syndrome requires that two or more of the following metabolic abnormalities occur within 3 days before or up to 7 days after the initiation of therapy. Morris and Philip M. Stewart Cameron George S. Allopurinol is a medication which inhibits xanthine oxidase. Davies Purine Laboratory and Renal Unit Guys Hospital London Bridge London SEI 9RTUK Received 1 May 1986.



























Post a Comment for "Allopurinol Tumor Lysis Syndrome"