Thoracic Outlet Syndrome Differential Diagnosis
Thoracic outlet syndrome differential diagnosis. Pediatric thoracic outlet syndrome. Each type has different symptoms and physical findings by which the three types can easily be identified. Ptosis of the eye and a constricted pupil miosis are signs of Horners Syndrome that do not occur in thoracic outlet syndrome.
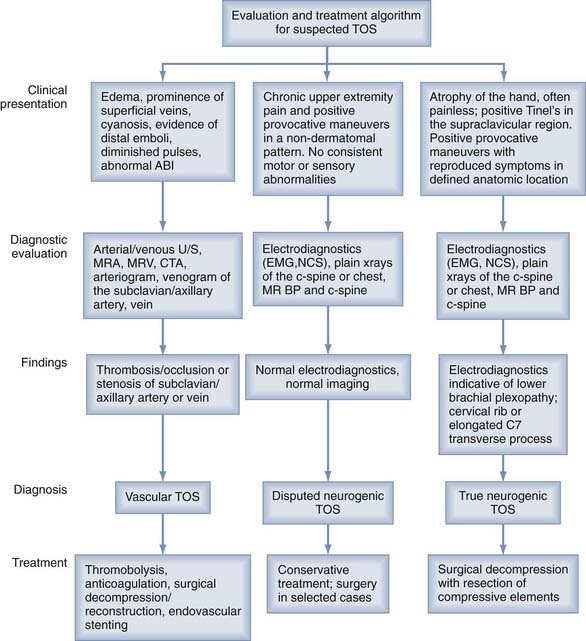
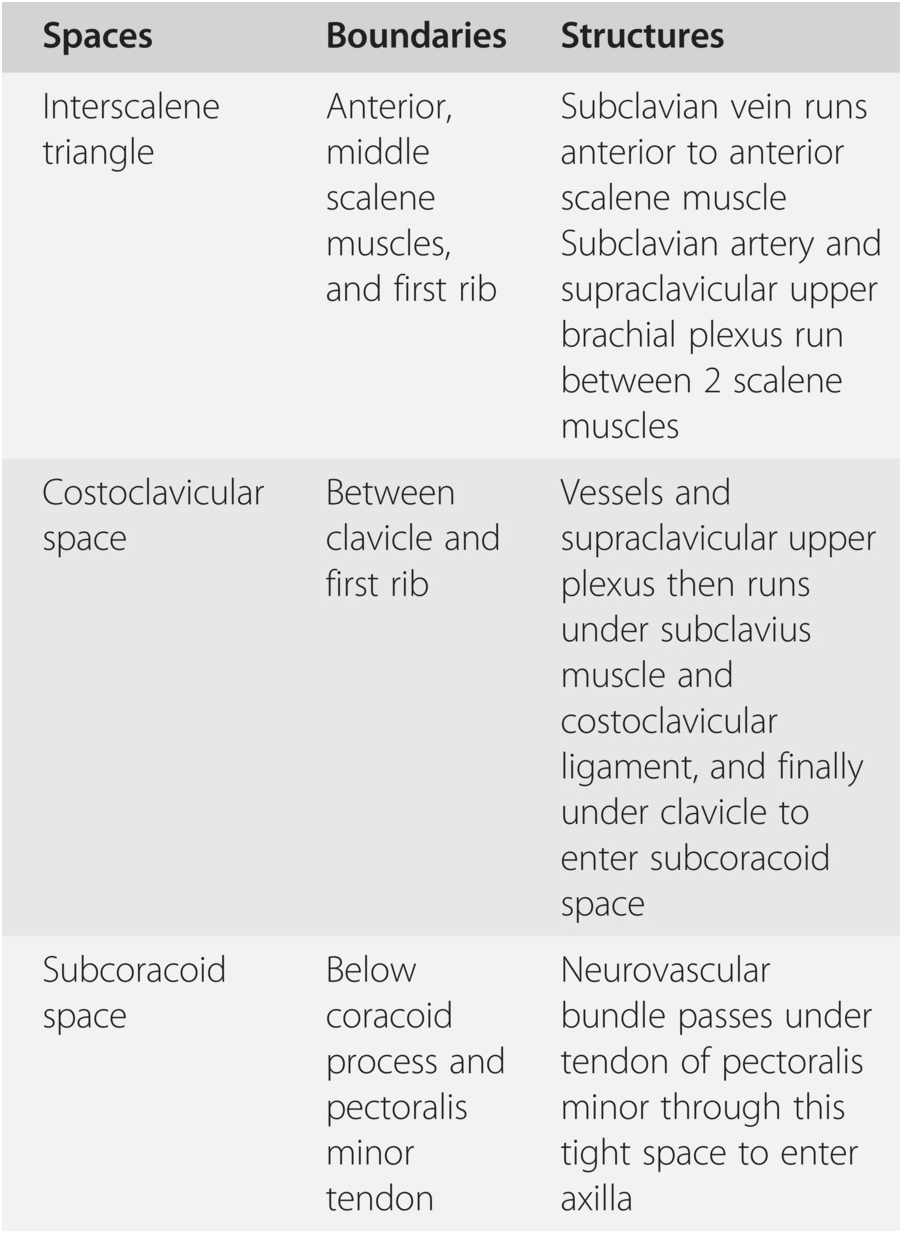
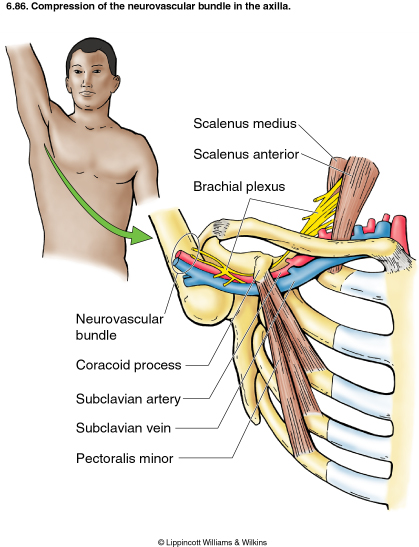
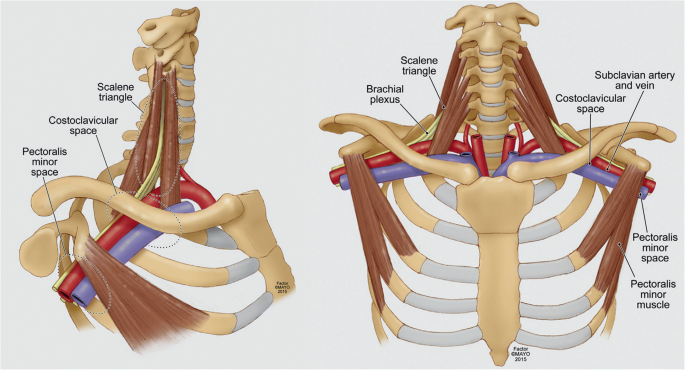
The prevalence of arterial TOS is undefined in the general population. The diagnosis of thoracic outlet syndrome TOS has long been a controversial and challenging one. Occlusion of the subclavian vein by way of the scalenes 1st ribanomalous rib or intra-venous blockage causes clinical VTOS.
Radiological autonomic and neurological testing is required to appropriately differentiate between Horners Syndrome and thoracic outlet syndrome. Thoracic outlet syndrome TOS is complex clinical entity characterized by various neurovascular signs and symptoms of the upper limb. It may be under-diagnosed.
Vascular symptoms including Raynauds phenomenon may occur in 10 of cases. Careful clinical assessment by history and examination may reveal the elements of forearm and upper arm symptoms with postural exacerbation which distinguish this condition from handarm vibration syndrome. Failed attempts at conservative management may be related to.
This section also includes a list of referral guidelines for patients presenting with symptoms in the chest. Thoracic outlet syndrome TOS is a cause of vascular and neurological compromise to the arm and hand and may manifest as Raynauds phenomenon. Neurogenic TOS NTOS is by far the mo.
T4 Syndrome - Differential Diagnosis of the thoracic spine Thoracic- T4 Syndrome The term T4 syndrome represents a clinical pattern of signs and symptoms that are described below namely hypomobility of the T4 segment. Diagnosis of thoracic outlet syndrome. Thoracic outlet syndrome TOS is characterized by pain paresthesia weakness and discomfort in the upper limb.
A rehabilitation program for thoracic outlet syndrome TOS should be designed based on results of the clinical examination that includes provocative testing. It is known that TOS is a cluster of neurological pain and vascular deficits that sit on a continuum from intermittent to permanent impairments.
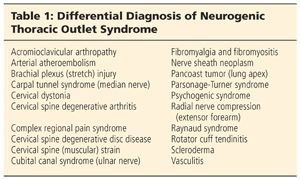
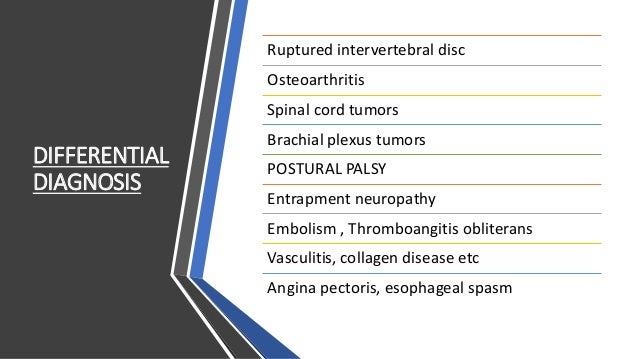
Differential Diagnosis Many conditions present similar to thoracic outlet syndrome.
Ptosis of the eye and a constricted pupil miosis are signs of Horners Syndrome that do not occur in thoracic outlet syndrome. Pediatric thoracic outlet syndrome. Take a look at the mind map for more information about each of these conditions. Furthermore there is a plethora of differential. This review was undertaken in order to clarify the diagnostic and investigative features of TOS that may differentiate it from hand-arm vibration syndrome. Arthur LG Teich S Hogan M Caniano DA Smead W. The diagnosis of thoracic outlet syndrome TOS has long been a controversial and challenging one. A disorder with serious vascular complications. This statistic shocked me.
Take a look at the mind map for more information about each of these conditions. Failed attempts at conservative management may be related to. Mobilization of upper thoracic vertebrae often reproduces or eliminates the patients symptoms. Despite common presentations with pain in the neck and upper extremity there are a host of presenting patterns that can vary within and between the subdivisions of neurogenic venous and arterial TOS. It is known that TOS is a cluster of neurological pain and vascular deficits that sit on a continuum from intermittent to permanent impairments. Occlusion of the subclavian vein by way of the scalenes 1st ribanomalous rib or intra-venous blockage causes clinical VTOS. A disorder with serious vascular complications.
































Post a Comment for "Thoracic Outlet Syndrome Differential Diagnosis"