Parenteral Nutrition Associated Liver Disease
Parenteral nutrition associated liver disease. PNALD develops in 40-60 of infants on long-term parenteral nutrition compared with 15-40 of adults on home parenteral nutrition. However it does have serious adverse effects including parenteral nutrition-associated liver disease PNALD. We previously Ng K et al.
Reported prevalence rates of. Clinical presentation is different in adults and infants. PN parenteral nutrition PNAC parenteral nutrition-associated cholestasis PNALD parenteral nutrition associated liver disease REE resting energy expenditure Fig.
However it does have serious adverse effects including parenteral nutrition-associated liver disease PNALD. Clinical nutrition in liver disease. Parenteral nutrition PN-associated liver disease PNALD refers to liver dysfunction caused by intestinal failure or inability to digest and absorb nutrients that oc-.
Parenteral nutrition associated liver disease PNALD is an important problem in patients who require longterm parenteral nutrition as well as in preterm infants. Parenteral Nutrition Derangement of liver function tests LFTs is common amongst patients receiving parenteral nutrition PN and is currently more common in the paediatric population. Parenteral nutrition PN provides life-saving nutritional support in situations where caloric supply via the enteral route cannot cover the necessary needs of the organism.
Parenteral nutrition-associated liver disease PNALD has been common in patients who require long-term parenteral nutrition. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr 40. Statement 1 In patients with cirrhosis a high prevalence of malnutrition protein depletion and trace element deficiency should be antici-pated.
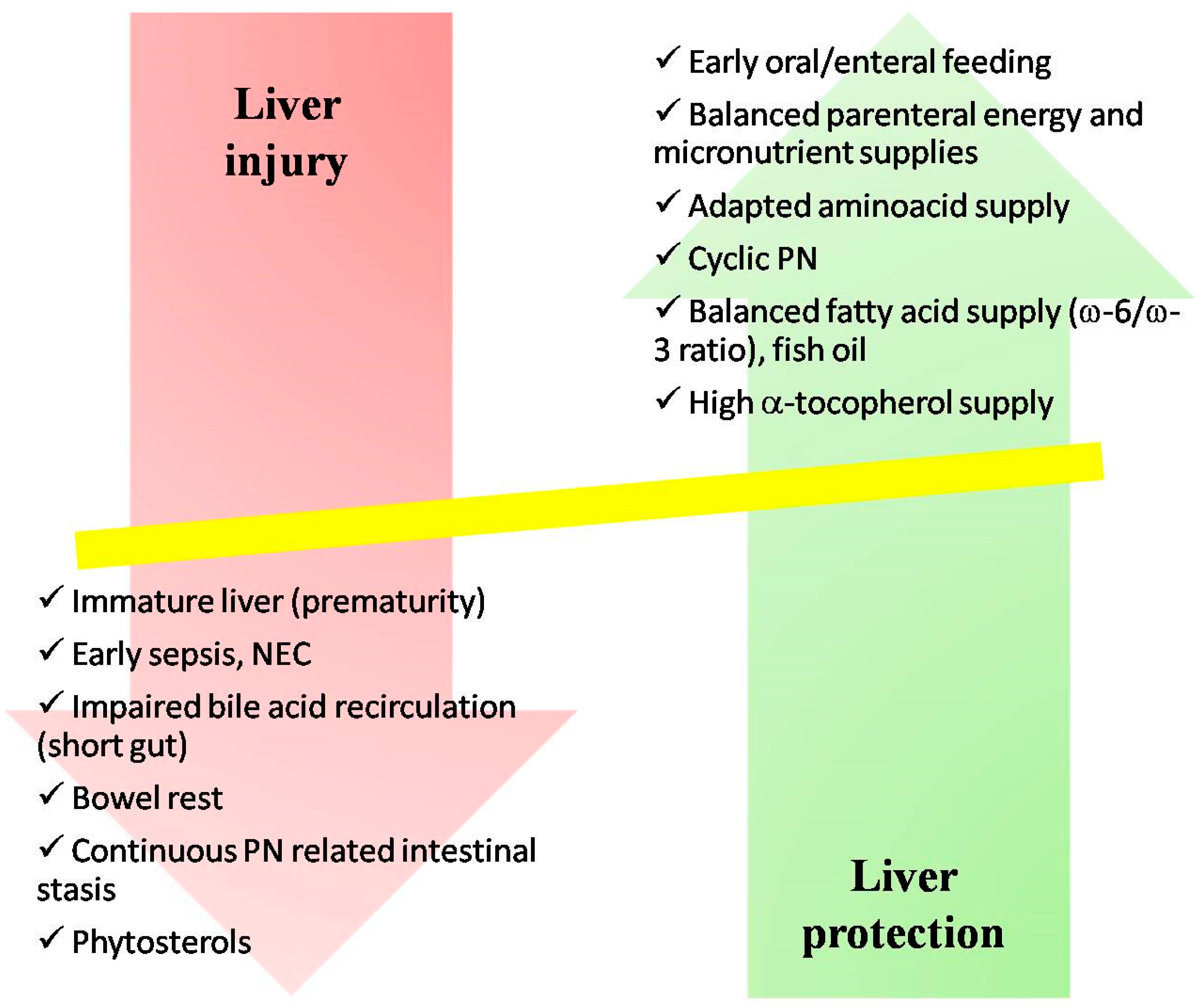
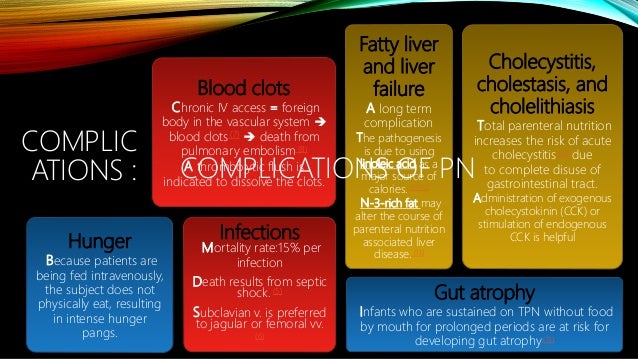
Liver disease is relatively common during parenteral nutrition PN. There is a broad spectrum of disease ranging from transient elevation in the liver enzymes in those receiving short-term PN through to cirrhosis and. Longterm use of parenteral nutrition PN may elicit complications including PNassociated liver disease PNALD which may yield critical outcomes.
Nutrition associated liver disease MP. Complementary to the ESPEN guideline on enteral nutrition of liver disease LD patients the present guideline is intended to.
However it does have serious adverse effects including parenteral nutrition-associated liver disease PNALD.
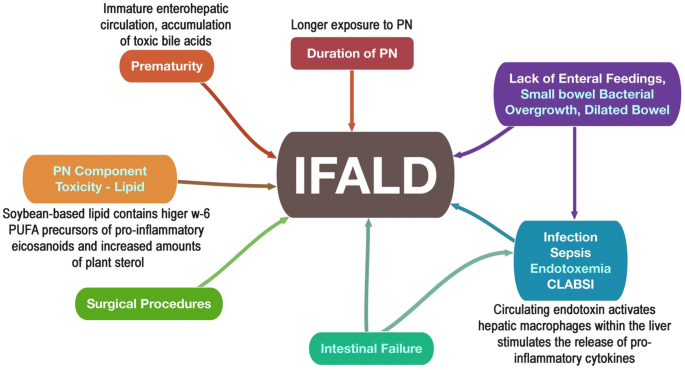
However it does have serious adverse effects including parenteral nutrition-associated liver disease PNALD. Nutrition associated liver disease MP. Statement 1 In patients with cirrhosis a high prevalence of malnutrition protein depletion and trace element deficiency should be antici-pated. However it does have serious adverse effects including parenteral nutrition-associated liver disease PNALD. Substantial data has implicated components of parenteral soybean oil in the pathogenesis of parenteral nutrition-associated liver disease PNALD. Parenteral nutrition PN provides life-saving nutritional support in situations where caloric supply via the enteral route cannot cover the necessary needs of the organism. We hypothesize that this occurs via vitamin E. There is a broad spectrum of disease ranging from transient elevation in the liver enzymes in those receiving short-term PN through to cirrhosis and. Parenteral nutrition provides nutritional support for those patients with prematurity malabsorption severe inflammatory bowel disease necrotizing enterocolitis congenital gastrointestinal disorders and extensive gastrointestinal surgery by intravenous infusion of macronutrients glucose lipid and amino acids micronutrients vitamins and minerals electrolytes and water.
Parenteral nutrition PN provides life-saving nutritional support in situations where caloric supply via the enteral route cannot cover the necessary needs of the organism. We hypothesize that this occurs via vitamin E. Clinical Nutrition 39 2020 3533e3562 3534. Substantial data has implicated components of parenteral soybean oil in the pathogenesis of parenteral nutrition-associated liver disease PNALD. Nutrition associated liver disease MP. This study intended to investigate the development of complications associated with commercial premixed PN in adult patients. Clinical nutrition in liver disease.







































Post a Comment for "Parenteral Nutrition Associated Liver Disease"