What Is Airspace Disease In Lungs
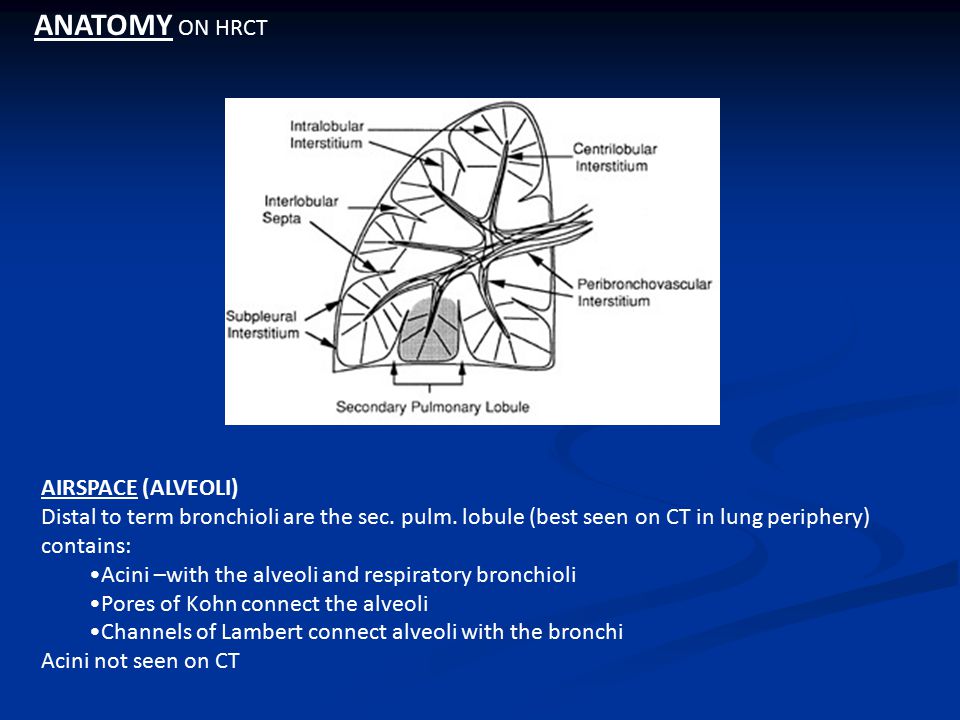
What is airspace disease in lungs. It is one of the many patterns of lung opacification and is equivalent to the pathological diagnosis of. Low attenuation regions are abnormal and reflect decreased perfusion of the poorly ventilated regions eg. Ground-glass opacification is a relatively common sign of airspace disease.
Historically the term acinar. Airspace disease can be acute or chronic and commonly present as consolidation or ground-glass opacity on chest imaging. In here pneumothorax occurs as a secondary condition.
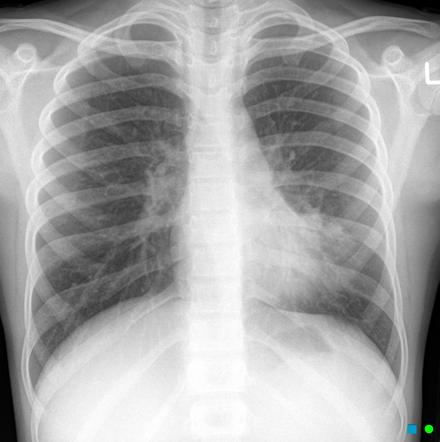
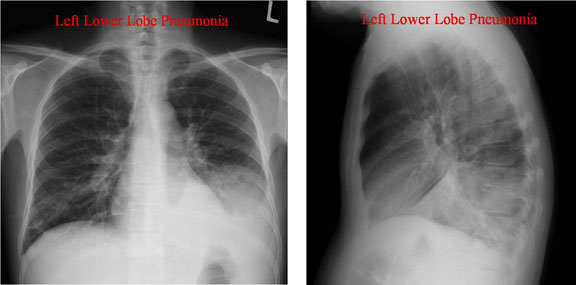
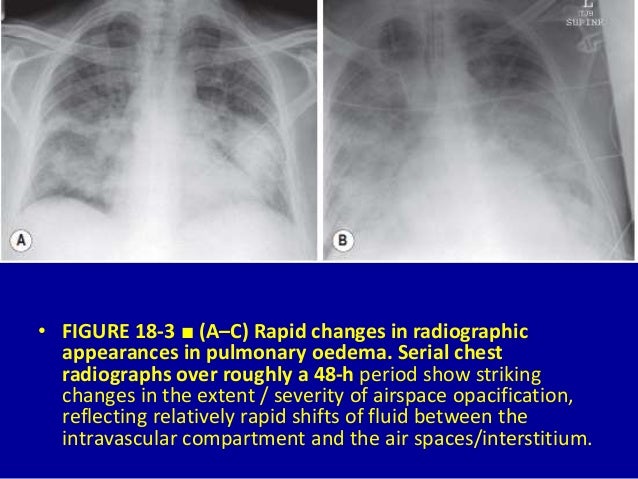
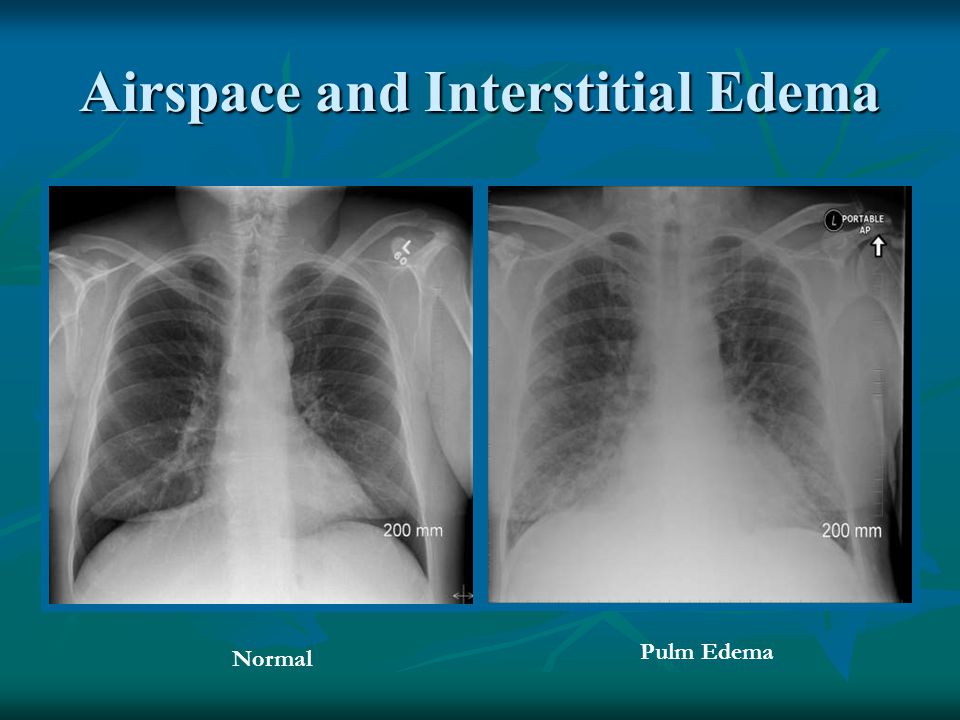
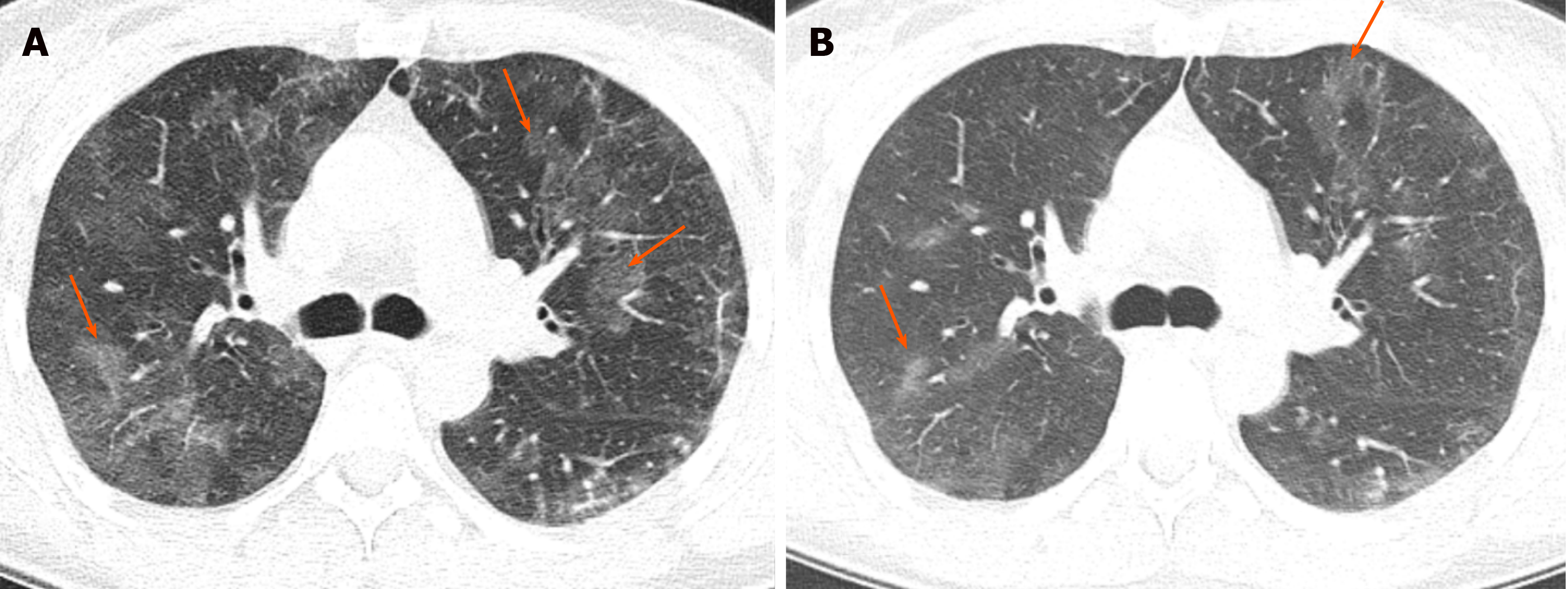
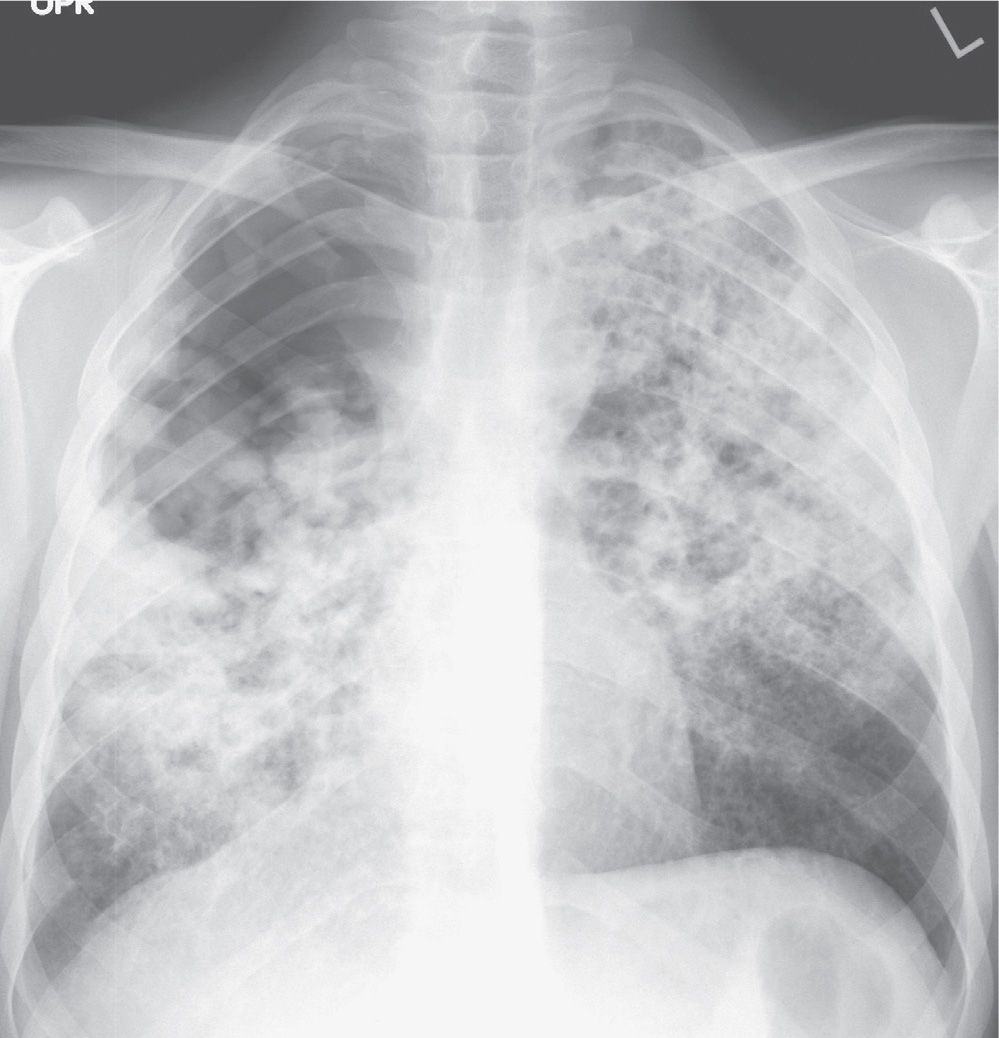
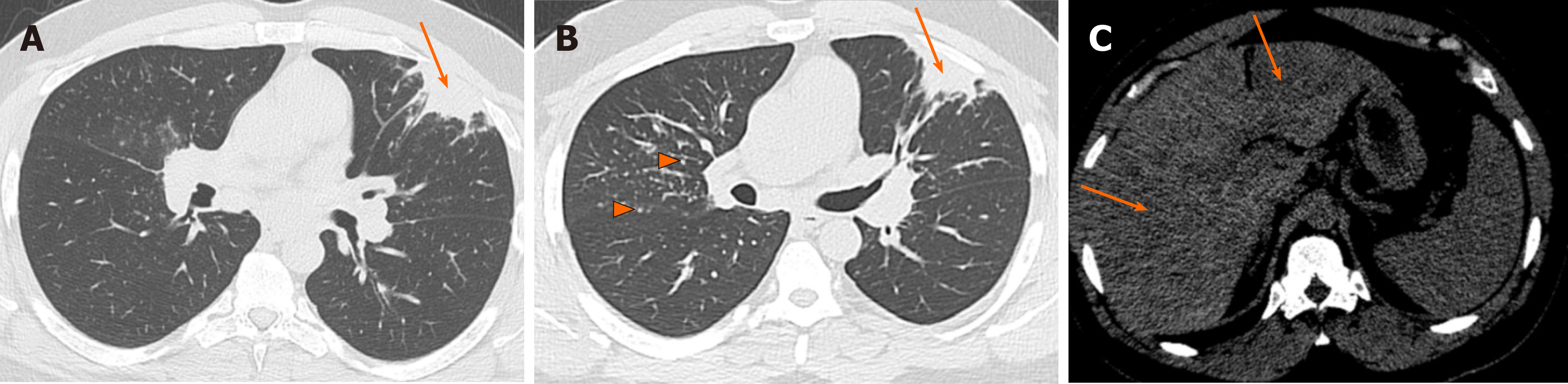
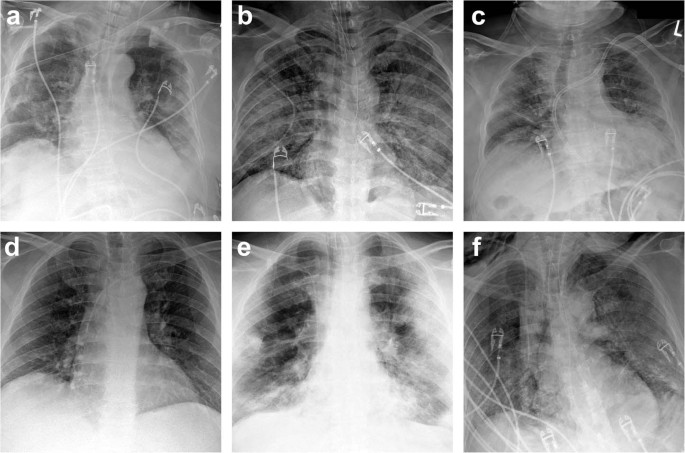
Airspace disease is considered chronic when it persists beyond 4-6 weeks after treatment. These fluffy opacities tend to be confluent meaning they blend into one another with imperceptible margins. Consolidation or ground-glass opacity occurs when alveolar air is replaced by fluid pus blood cells or other material.
Low attenuation regions are abnormal and. Bibasilar airspace disease also known as alveolar lung disease is a condition of the lungs in which the air spaces are swollen and contain fluid. Occlusive vascular disease can be termed a mosaic perfusion pattern in this setting 7.
Bronchiectasis cystic fibrosis constrictive bronchiolitis. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Airspace disease can be acute or chronic and commonly present as consolidation or ground-glass opacity on chest imaging.
Some examples of COPD include asthma bronchitis and emphysema. It is by far the most common reason of the presence of air in lungs. On plain radiography ground-glass.
Learn what to expect if your doctor tells you that you have one of the four main types of cystic lung disease a condition that causes cysts to grow in your lungs. Atelectasis is a lung condition that happens when your airways or the tiny sacs at the end of them dont expand the way they should when you breathe.
Low attenuation regions are abnormal and reflect decreased perfusion of the poorly ventilated regions eg.
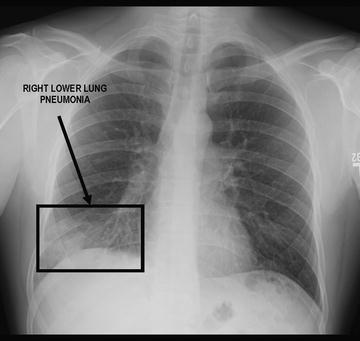
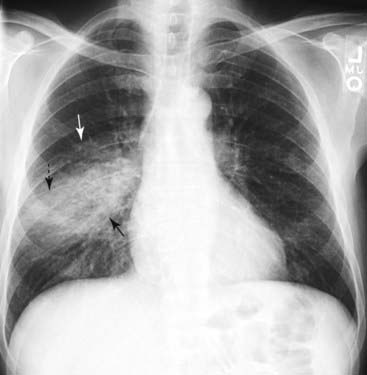
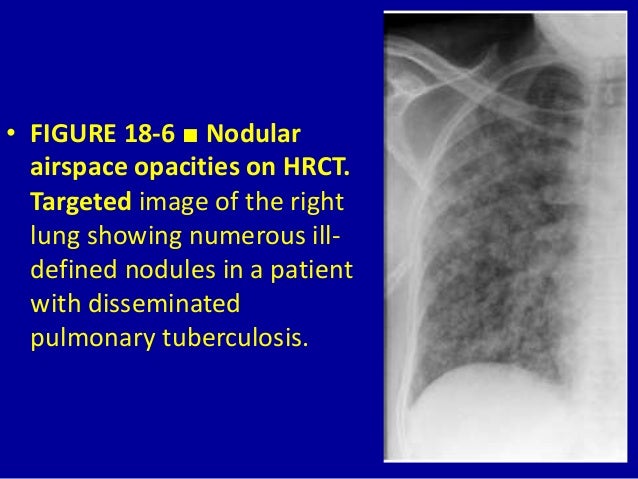
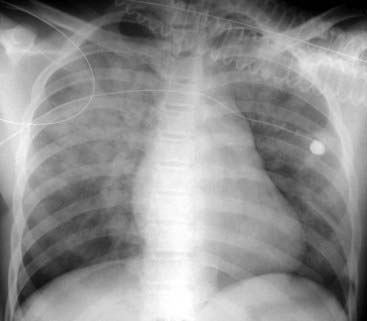
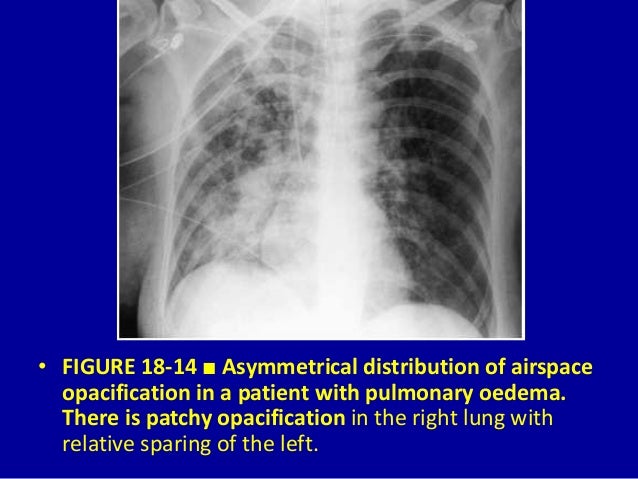
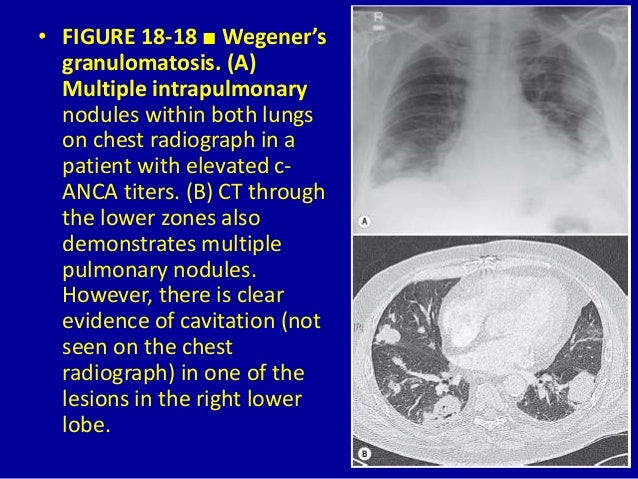
Airspace disease can be acute or chronic and commonly present as consolidation or ground-glass opacity on chest imaging. Interstitial lung disease is an umbrella term that includes many different conditions. Occlusive vascular disease can be termed a mosaic perfusion pattern in this setting 7. The opacified acini become confluent producing a fluffy homogeneous radiographic pattern characteristic of airspace disease as seen in Fig. It is typically defined as an area of hazy opacification x-ray or increased attenuation CT due to air displacement by fluid airway collapse fibrosis or a neoplastic process. Some examples of COPD include asthma bronchitis and emphysema. Airspace disease can be acute or chronic and commonly present as consolidation or ground-glass opacity on chest imaging. It is by far the most common reason of the presence of air in lungs. Bronchiectasis cystic fibrosis constrictive bronchiolitis.
Less common causes include bleeding or protein secretions within the lungs. In here pneumothorax occurs as a secondary condition. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Diagnosed with patchy airspace disease in my left lung also moderate to Patchy airspace disease in the right What treatments are there for this and is it a life-threatening disease if so what is the lifespan thank you so very much Tamsey Laura fields. Interstitial lung disease is an umbrella term that includes many different conditions. Some examples of COPD include asthma bronchitis and emphysema. It is one of the many patterns of lung opacification and is equivalent to the pathological diagnosis of.


























Post a Comment for "What Is Airspace Disease In Lungs"